Perform Univariate Kriging
SpaceStat provides many ways to customize the kriging procedure to various types of data. The Task Manager separates the method into related panels that we describe below.
Source and Destination Geographies
The first panel contains the source geography and dataset that you want to interpolate to the destination geography. If the source and destination geographies are the same, cross-validation is conducted and prediction statistics (e.g. mean prediction error) are reported in the Log view window. The exception to this is if population adjustment (Poisson Kriging) or the factorial kriging option is selected.
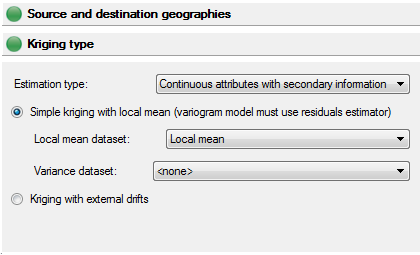
Kriging Type
The second panel in the kriging method defines the kriging type. The options available change depending on whether or not secondary information is available.
If the estimation is to be Continuous attributes without secondary information, the kriging options available are simple kriging, ordinary kriging, and kriging with a trend.
In addition, these three methods can also incorporate an estimation of spatial components (factorial kriging). If the estimation is ordinary kriging, a Poisson population adjustment method can be incorporated as well.

If there is secondary information available, the user may employ simple kriging with a local means dataset or kriging with external drifts. Instead of specifying a single global mean, the local means dataset defines a mean value that varies across the landscape. An optional variance dataset defines the variance on the local means. Similarly, the drift datasets define spatial trends across the landscape.
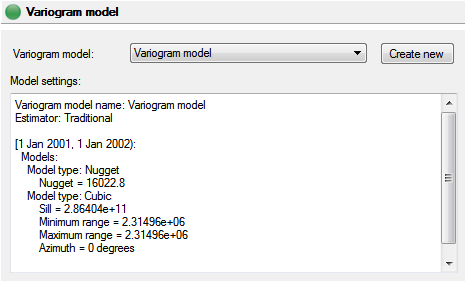
Variogram model
This panel allows the user to choose an existing variogram model or to create a new one. Valid variogram models will appear as options in the drop down menu. Note that certain kriging options will require specific parameters in the variogram model. Simple kriging, for example, may not use a power model in the corresponding variogram. The user can view these models by opening them in the Variogram Model Dialog via the Variogram Models view.
Search Strategy
This panel allows the user to specify the window in which the observations are taken.
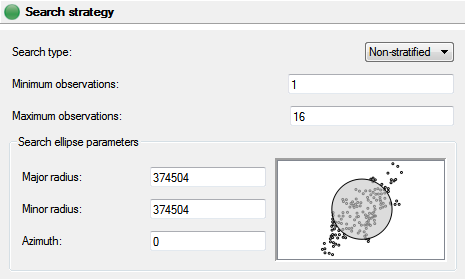
There are three types of search strategies provided by the Univariate kriging method: non-stratified, quadrant, and octant. For the non-stratified option SpaceStat will attempt to locate the nearest n points in any direction around the target point where n is the maximum count specified. If the number of neighbors found is less than the minimum count specified, or n points can't be found the target point will be skipped and the value will be set to missing. Note that neighboring points which hold missing values will be skipped. In the case where there are distance ties for the last (n-th) point all the neighboring points at the n-th distance will be included.
When using a stratified search SpaceStat tries to choose neighboring points more equitably distributed around the target. In this case the minimum-observations parameter is the total number of neighbors desired and the maximum-observations parameter indicates the maximum number of points to fall in each quadrant or octant. This means that neighbors found in a sector that is already full will be skipped and the search will continue outward from the target point. If the minimum total number of neighbors can't be found the location will be set to missing.
The search ellipse parameters allows the user to define the maximum distance to look for neighbors and also to accommodate an anisotropic distribution of data. The minimum and maximum radius specify the shape and size of the search ellipse, and the angle specifies the orientation. If the two radii are equal a circular search is performed. The search ellipse is overlaid on the source geography to facilitate the selection.
Back Transform
This panel allows a user to specify a back transform to transformed data. If a user chooses to apply a back transform, they may choose between e^x and 10^x or the normal score back transform.
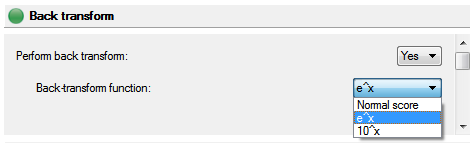
If the user chooses e^x or 10^x, there are no further requirements for the back transform. The normal score back transform has a few more parameters associated with it.
Other Settings
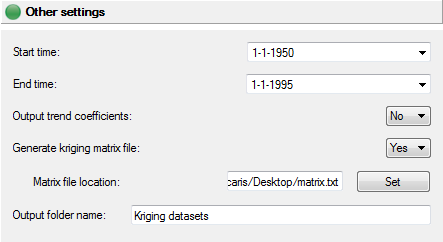
Select the start and end time for the interpolation (useful when several time periods with different semivariogram models are available).
Trend coefficient datasets can be created and a text file with the kriging matrix and kriging weights for each destination geography object can be exported for further analysis.
You may also change the name of the output folder.
For an example of a kriging analysis, try the New England kriging tutorial.