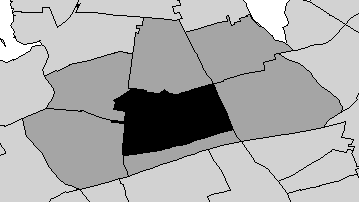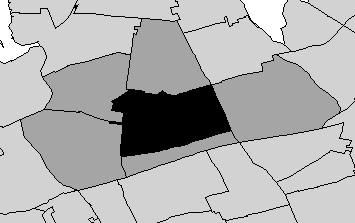
ClusterSeer can derive neighbor relationships from a file of polygons. In essence, ClusterSeer will evaluate whether the polygons share a border with each other or overlap. If they share a border or overlap, they are considered neighbors. In order to derive neighbor relationships from polygons in shapefile format, you must specify how ClusterSeer should evaluate these relationships. While it may seem like a trivial concept, in fact the specification of neighbor relationships can influence the outcome of statistical analyses.
Two options are available—rook and queen—their names come from the movements of chess pieces. The rook can move only to polygons that share a border of some length with its current polygon. In the figure below, the rook, illustrated as the central black polygon, can move only to the five dark gray polygons that share borders of some length with it. The queen in the second figure below can move to any polygon that shares even a point-length border. So, she can move to the rook's polygons and to any polygon that shares a corner (one vertex) with her current polygon. That gives the queen a total of six adjacent polygon neighbors.
Thus, rook is a more stringent definition of polygon contiguity than queen—for rook the shared border must be of some length, whereas for queen the shared border can be as small as one point.