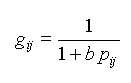
You can use two types of generator matrices for randomization, a distance decay matrix which BoundarySeer can calculate, or you may define your own generator matrix.
Distance Decay.
To account for spatial autocorrelation, the probabilities in the generator matrix are such that observation vectors are likely to be assigned to locations that are close to where they were originally observed. Using this model, the generator matrix can be calculated as a function of the proximity matrix, whose elements pij are the geographic distances between locations i and j.
BoundarySeer can calculate the proximity matrix and then use a distance decay function to calculate a generator matrix according to your specifications. To do this, select the 'Restricted: Distance decay' option as the randomization type, and then enter the distance decay constant. BoundarySeer uses the distance decay constant to calculate probabilities according to the equation
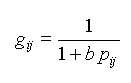
User Defined. You may also define your own generator matrix for BoundarySeer to use during randomization. The matrix must be stored in a space- or tab-delimited text file, where each row of the file contains the elements for each corresponding row of the matrix. Any user-defined matrix is subject to these constraints:
The matrix must be N X N, where N is the number of locations in the data set to be randomized.
The order of locations in the matrix should correspond to the order of locations in your original input file. If you are unsure of the ordering, check your original file, or view a table of the data in BoundarySeer.
The generator matrix file contains only the elements of the matrix and appropriate delimiters (space or tab); no header information is permitted.
It is advised that the matrix contain only nonzero elements. However, if there are zeroes, they must be arranged in the matrix so that, during the Monte Carlo process, BoundarySeer is never asked to assign observation vector Zi to location j if gij = 0. To ensure that your matrix fits this description, do the following.
First, make sure the diagonal elements are non-zero.
Next, count the number of non-zero elements in each row.
Put these counts into a list. Eliminate any counts of zero (corresponding to rows with only zero elements). Sort the remainder of the list.
Each value must occur in the list the number of times equal to its value. For example, a count of '3' (a row with 3 non-zero elements) must occur exactly 3 times in the list. A count of '2' must occur exactly twice. If there is any deviation from this rule, then the matrix is NOT a valid generator matrix.
Repeat steps ii-iv, counting the number of non-zero elements in each column.
To use your own generator matrix during randomization, select the 'Restricted: Generator matrix from file' option as the randomization type, and then enter the file name that contains the matrix. BoundarySeer will check the matrix and alert you if there are violations of any of the above rules.
See also: