Non-geographical Weights in Regression
In geographically weighted regression (GWR), a distance function is used to "weight" values observed at neighboring locations so that you can identify local patterns in relationships between independent and dependent variables. In a similar way, you can weight observations in an aspatial regression or GWR so that some observations "matter" more than others when building a regression model. One example of when you might want to use a weight dataset is in a regression analysis using disease rate data. In many cases, these datasets show strong variation across space in the population size, which acts as the denominator in the rate calculation. However, the higher the population size, the more confident you can be that your rate is not overly influenced by just a few occurrences of the disease (i.e., the small numbers problem, as described in this tutorial). So, if you are working with rates and have a population size dataset for the same geography, you may want to try a model that includes this weighting factor.
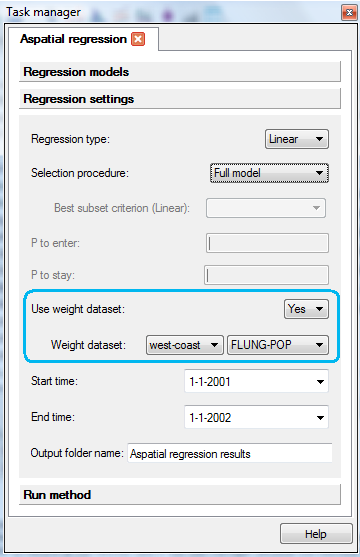
You would enter the weight dataset in the "Regressions settings" page of the Task manager.