The crux of Diggle's method is to compare two spatial models for case locations, one with no relationship to the focus (the null hypothesis) and one where the pattern of the disease depends on the focus. Diggle and Rowlingson (1994) compare the two models using a generalized log likelihood test (GLRT). Essentially the test evaluates which model better explains the data.
The generalized log likelihood test is:
![]()
Where ![]() is the log likelihood of the alternative hypothesis, and
is the log likelihood of the alternative hypothesis, and ![]() is the log likelihood for the null hypothesis, below.
is the log likelihood for the null hypothesis, below.
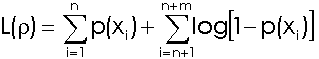
![]()
The case and control subject locations represent the complete set of locations under study (xi). In the above equations, the p(xi) functions describe the probability that location i is the location of a case subject.
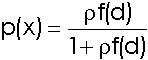
The significance of D is obtained with reference to the Chi-squared distribution with 2 degrees of freedom.