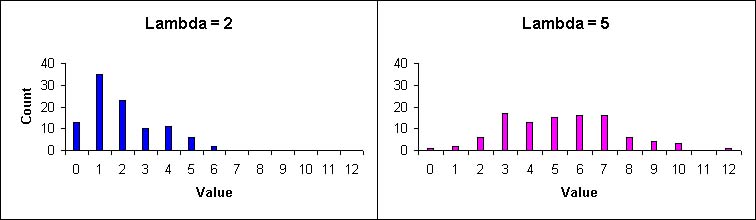
The null hypothesis of a Poisson disease rate is usually a good representation of randomly distributed non-infectious rare diseases (Waller and Jacquez 1995). It is used in many cluster detection methods in ClusterSeer, including Besag and Newell's method. A Poisson function can be described by one parameter, lambda ( ![]() ), the mean and variance of the distribution. Within ClusterSeer, lambda is the average or expected case count, calculated from the average or expected disease frequency multiplied by the population-at-risk.
), the mean and variance of the distribution. Within ClusterSeer, lambda is the average or expected case count, calculated from the average or expected disease frequency multiplied by the population-at-risk.
Poisson point process models are used for null and alternative spatial models in Diggle's Method and Ripley's K-function. Poisson point processes produce sets of points with a given intensity ( ![]() , the mean and variance of the Poisson distribution), an expected number of points or cases per unit area.
, the mean and variance of the Poisson distribution), an expected number of points or cases per unit area.