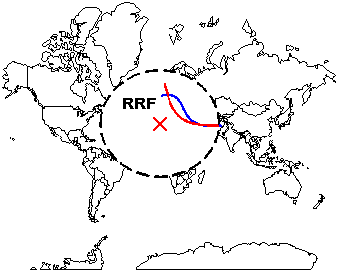

Bithell's (1995, 1999) linear risk score test is a spatial, focused cluster detection method appropriate for group-level data. This test is sensitive to excess risk near a point source exposure (focus), and it considers the spatial relationship of the cases to the focus.
The method scores each disease case with a risk score, the logarithm of the relative risk in that region. The test statistic is the sum of these risk scores. The change in relative risk from the focus can be evaluated graphically in plots of the relative risk function (RRF). Because of the linear structure of the statistic T, Bithell calls this type of test a linear risk score (LRS) test.
The test was originally presented in a paper evaluating the pattern of childhood leukemia and non-Hodgkins lymphoma near nuclear plants in the U.K. (Bithell 1995).