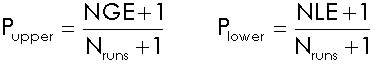
The P-value is the relative ranking of the test statistic among the sample values from the Monte Carlo randomization. You can calculate P-values to see whether observed values are unusually large or small for the null distribution. This calculation compares the observed value to the upper and the lower tails of the null distribution. Most tests in ClusterSeer explore whether the observed value is unusually large for the distribution, using Pupper only.
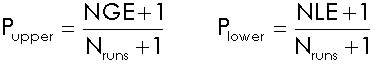
where Nruns is the total number of Monte Carlo simulations, NGE is the number of simulations for which the statistic was greater than or equal to the observed statistic, and NLE is the number of simulations for which the statistic was lower than or equal to the observed statistic. One (1) is added to the numerator and denominator because the observed statistic is included in the reference distribution.