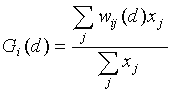
|
Ho |
There is no clustering of high or low values within the specified distance of location i, test statistic is close to zero. |
|
Ha |
There is clustering of high or low values within the specified distance of point i. A significant positive value implies a clustering of high values, and a significant negative value indicates a clustering of low values. |
The statistic measures the degree of association that results from the concentration of weighted points or region centroids and all other weighted points within distance d from the point of study (Getis and Ord 1992).
The basic statistic is defined as:
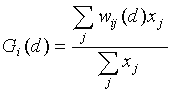
In this equation, the xj are the weighted values of the points in the study area. wij is a binary, symmetric weights matrix with ones for all points j within distance d of point i and zeros otherwise.
There are two variants of the local G statistic. The Gi statistic excludes the value at i from the summation and is used for spread or diffusion studies, while the Gi* includes the value at i in the summation and is most often used for studies of clustering.
Essentially, the Gi statistic represents a ratio of the values within distance d of point i to the sum of all values minus the value at point i. The Gi* includes all values.
Significance
In (Ord and Getis 1995) the authors reformulated the statistic so that the results are given in standard normal variants. The statistic is normally distributed, and can be used for normal as well as skewed frequency distributions of the underlying variable. However, when the number of neighbors is small the statistic is less reliable.
The significance of each local G value may also be evaluated using a Monte Carlo randomization procedure.